Day 13 in MIT Sloan Fellows Class 2023, Applied Economics-2
What makes the market imperfect
In reality, the market is not perfect at all, but we learn perfect market first in economics. The perfect market contains fundamental of market dynamics such as supply and demand balance. So, what makes the market imperfect?
- Market power
- Existence of external costs and benefits(externalities)
- Information problems (inequality in information distribution)
- Public goods(non-excludable or non-rival or both)
- Factors of production cannot always be moved(capital, land etc)
- Transaction costs
In a nutshell, perfect market theory ignores these situations.
Externalities
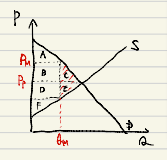
The starting point of market externalities is marginal private cost/benefit does not equal marginal social cost/benefit.

Firstly, negative externality affects supply curve and decreases optimal quantity. It describes our current society overproducing many products. The pink area is the cost of negative externality. The typical example of a negative externality is pollution.
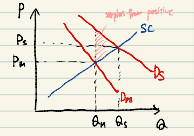
The other is positive externality. It shifts demand curve. The example is opensource R&D etc.
Monopoly